Email Us Now: info@gcfdl.com
Genuine Bank Guarantee Provider
Who is a Genuine Bank Guarantee Provider?
A genuine bank guarantee provider is a bank or financial institution like General Credit Finance and Development Limited that issues Bank Guarantees (BG), Standby Letters of Credit (SBLC) and other bank instruments for customers. These genuine bank guarantee providers and other financial institutions help clients secure loans and project financing, activate credit lines, collateral transfer, trade finance and enhance creditworthiness.
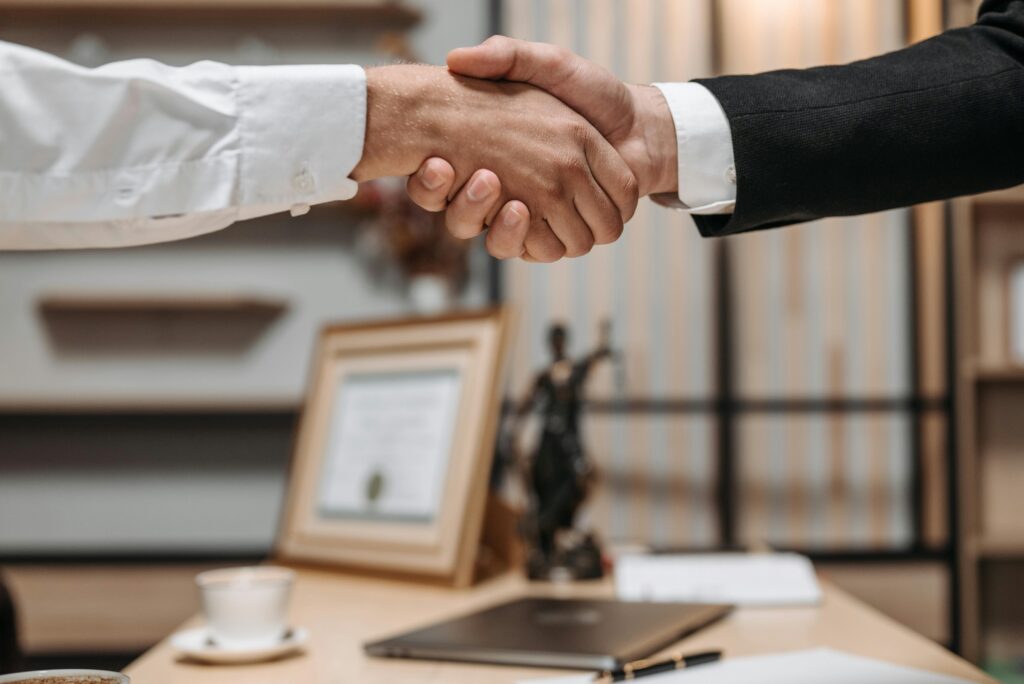

What is a bank guarantee?
A bank guarantee is a guarantee given by the bank on behalf of the applicant to cover a payment obligation to a third party. It is an assurance to a beneficiary that the bank will uphold a contract if the applicant and counterparty fail to do so. In other words, the bank offers to stand as the guarantor on behalf of a business customer in a transaction.
Bank guarantees are issued by banks and financial institutions (genuine bank guarantee providers) and typically used outside the United States, allowing a bank’s client to purchase goods, acquire equipment, or engage in international trade. If the client defaults on a debt or fails to deliver agreed-upon goods, the bank steps in to cover the obligation.
For instance, consider Emerald Company, a newly established textile factory aiming to purchase fabric raw materials worth US$7,000,000. The raw material vendor demands a bank guarantee from Emerald Company to cover payments before shipment. Emerald Company obtains this guarantee from its lending institution, which holds its cash accounts. The bank essentially cosigns the purchase contract. If Emerald Company defaults, the vendor can claim the payment from the bank.
Types of Bank Guarantees
Advance Payment Guarantee: Ensures reimbursement of advance payment if the supplier fails to deliver.
Performance Guarantee: Covers performance-related obligations.
Payment Guarantee: Ensures payment to the seller if the buyer defaults.
Bid Bond Guarantee: Protects against the risk of the successful bid not being honored.
Financial Guarantee: Guarantees repayment of financial obligations.
Tender Guarantee: Similar to Bid Bond, ensures the bid’s commitments.
Customs Guarantee: Covers customs duties and taxes.
Foreign bank guarantee: A foreign bank guarantee is provided by a bank on behalf of a borrower. This will be offered on behalf of the foreign beneficiary or creditor.
Retention Guarantee: Ensures the retention amount is withheld by the employer for any defects.
Shipping Guarantee: Facilitates the release of goods without a Bill of Lading.
Performance Bond: Guarantees project completion within agreed timelines.
Loan Guarantee: Covers loan repayment to the bank.
Rent Guarantee: Ensures payment of rent by the tenant.
Direct Guarantee: Issued directly by the bank in favor of the beneficiary.
Understanding Bank Guarantees
A bank guarantee is a commitment by a lending institution to cover a loss if a business transaction doesn’t proceed as expected. This ensures the buyer receives compensation if a party fails to deliver goods or services as agreed or fulfill contractual obligations.
In countries like Spain, the U.K., and other non U.S. regions, financial institutions, and intermediaries often rely more heavily on bank guarantees in commercial transactions. However, a bank guarantee can also assist individuals in renting properties.
Also known as a standby letter of credit or a bond, a bank guarantee from a reputable institution can help establish business relationships, increase access to cash flow and capital, protect your business from losses, and open up international opportunities.
Do Banks in the U.S. Issue Bank Guarantees?
Banks in the U.S. generally do not issue bank guarantees. Instead, they provide standby letters of credit, which serve the same purpose by ensuring the beneficiary gets paid if the client cannot meet their obligations. It’s a similar safety net, just under a different name.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bank Guarantees
Advantages:
- Reduced Financial Risk: Bank guarantees lower the financial risk involved in business transactions.
- Encourages Expansion: Due to low risk, sellers and beneficiaries are more inclined to expand their business on a credit basis.
- Low Fees: Banks generally charge low fees for guarantees, which benefits even small-scale businesses.
- Increased Credibility: When banks certify the financial stability of a business, its credibility increases, leading to more business opportunities.
- Quick Processing: Guarantees require fewer documents and are processed quickly by banks if all documents are submitted.
Disadvantages:
- Rigid Assessments: Banks can be very strict in assessing the financial position of the business, making the process complicated and time-consuming.
- Difficult for Loss-Making Entities: Entities that are not financially strong may find it hard to obtain a bank guarantee.
- Collateral Security: For high-value or high-risk transactions, banks may require collateral security, making it challenging for some businesses to avail of such guarantees.
Pros of Bank Guarantees:
- Lower Costs: Bank guarantees are cost-effective, with banks charging between 0.5% to 1% of the guaranteed amount.
- Better Cash Flow Management: Eliminates the need for advance payments, helping businesses manage cash flow better.
- Increased Opportunities: Improves the creditworthiness of small and medium enterprises, expanding their business opportunities.
- Streamlined Process: Once due diligence is completed, the process to obtain a bank guarantee is straightforward and quicker compared to loans and overdrafts.
- Signaling Effect: Being issued a bank guarantee by a reputed bank signals financial stability, helping companies obtain funds at lower costs.
Cons of Bank Guarantees:
- Difficult to Obtain: Securing a bank guarantee is seamless only for businesses with strong financials. Those with unpredictable cash flow may struggle.
- Collateral Required: Banks often require significant collateral, making it hard for businesses without substantial assets to obtain guarantees.
- Regulatory Hassles: In countries with a history of fraud involving bank guarantees, strict regulations can make the process cumbersome. This can deter both banks from offering guarantees and businesses from seeking them.
Bank guarantee rules and regulations
Bank guarantees are subject to specific rules and regulations to ensure their transparency, fairness, and predictability in commercial transactions. Compliance with these regulations is essential for the integrity and effectiveness of bank guarantees as a financial instrument.
To maintain the credibility and effectiveness of bank guarantees, several rules and regulations guide their implementation. The Uniform Rules for Demand Guarantees (URDG), established by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), provide a globally recognized and consistent framework for using demand guarantees in international trade.
Adherence to these rules and regulations is essential for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of bank guarantees as a financial instrument in commercial transactions. They protect the interests of all parties, promote transparency, and help avoid legal disputes.
The difference between Bank Guarantee and a Letter of Credit
Many times, people get confused between a bank guarantee and a letter of credit. However, one should understand that both are pretty different.
A bank guarantee refers to a commercial or financial instrument that is provided by a bank, where the bank assures or guarantees a beneficiary that it will make the payment to the bank in case the actual customer fails to meet his or her obligations. The bank will pay on behalf of the customer who requests for a bank guarantee.
On the other hand, a letter of credit refers to a promise or commitment in writing made by a bank or any other financial institution or corporation to a particular seller that payment will be made to the seller if the seller completes performing whatever is mentioned in the letter of credit.
For the bank to make the payment on behalf of the original buyer, there should be a documentary proof that the seller has completed the transaction accurately by delivering the right product or service on time.
The seller will get a guarantee from the bank that the seller will definitely pay the amount on behalf of the original buyer once the obligations are fulfilled.
Under a bank guarantee, if the buyer is unable to make the payment to the seller or creditor, then the bank pays the fixed amount to the seller as the obligations of the contract are not met.
On the other hand, under a letter of credit, the bank makes the payment to the seller once he or she delivers. This is because the seller has completed fulfilling the required obligations.
Bank guarantees are competitively priced in nature generally. They are usually valid for a long period. The tenure of a bank guarantee is usually high. Moreover, bank guarantees are commonly accepted in almost all countries.
Major Differences Between Letter of Credit (LOC) and Bank Guarantee (BG)
| Particulars | LOC | BG |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Obligation accepted by a bank to pay a beneficiary if certain services are performed. | Assurance given by the bank to pay a specified amount in case of default by the applicant. |
| Primary Liability | Bank retains primary liability and later collects from the customer. | Bank pays only when the customer defaults. |
| Payment | Bank pays the beneficiary as due, without waiting for customer default. | Bank pays the beneficiary only if the customer defaults. |
| Way of Working | Ensures payment as long as services are performed per agreed terms. | Compensates for loss if the applicant fails to satisfy specified conditions. |
| Number of Parties Involved | Multiple parties: LOC issuing bank, customer, beneficiary, advising bank. | Three parties: banker, customer, beneficiary. |
| Suitability | More appropriate for import/export of goods and services. | Suitable for any business or personal transactions. |
| Risk | Bank assumes more risk than the customer. | Customer assumes the primary risk. |
Bank Guarantee Charges
BG charges typically depend on the risk the bank and bank guarantee provider takes on in each transaction. For instance, a financial BG assumes more risk than a performance BG, leading to higher fees. Fees are usually charged quarterly on the BG value, ranging from 0.75% to 0.50% during the validity period.
Additionally, the bank and bank guarantee provider may charge application processing, documentation, and handling fees. In some cases, the applicant must provide security, often 100% of the BG value. The bank might also accept collateral security or a cash margin in certain situations.
Monetization of Bank Guarantees (BG)- How do you monetize a bank guarantee
Monetizing a bank guarantee involves converting it into cash or legal tender. Bank guarantee monetization services are ideal for clients who want to discount or create an immediate non-recourse loan against a leased or owned bank guarantee.
Many customers contact us daily seeking to understand what bank instrument monetization is. A bank instrument is a financial instrument issued by banks, such as a bank guarantee or standby letters of credit.
Therefore, bank instrument monetization involves converting bank instruments, like bank guarantees or standby letters of credit, into funds through loans or lines of credit.
There are rules to follow to ensure the monetization process is successful. If a business wishes to monetize a bank guarantee in order to receive a loan or credit line, the wording (verbiage) must be specific to that of the bank guarantee.
Bank guarantee monetization is governed by ICC Uniform Rules for Demand Guarantees (URDG 758).
Top AAA Rated Banks We Issue and Monetize Bank Guarantees (BG) From:
Our SBLCs bank guarantees are issued by top-tier, AAA-rated banks such as:
- Barclays Bank London
- Deutsche Bank AG Germany
- HSBC Hong Kong
- Standard Chartered Bank
- Citibank New York
- Chase Bank
- Wells Fargo Bank
- Bank of America
- UBS Switzerland
As genuine bank guarantee providers and monetizers of standby letters of credit, we can monetize bank instruments (BGs/SBLCs) issued by the listed banks.
Conclusion
Since bank guarantees can help provide security for your business, it is important to learn about them and ensure you obtain a bank guarantee from a genuine bank guarantee provider like General Credit Finance and Development Limited. After looking at its definition and how it assists in covering your business against potential losses, the next step is to decide which guarantees would be the most appropriate for your business.
Contact us today to learn how an HSBC or Barclays bank guarantee could help take your business to the next level.

[…] adalah bank atau lembaga keuangan seperti General Credit Finance and Development Limited yang menerbitkan Jaminan Bank (BG), Surat Kredit Siap Pakai (SBLC), dan instrumen bank lainnya untuk pelanggan. Penyedia jaminan bank […]
[…] to be delivered in the future. If the buyer fails to fulfill their contractual obligations, the bank guarantees to reimburse the advance payment made to the […]